In recent years, navigating high-paced, high-stress environments has become a norm for many of us. From global pandemics, natural disasters, fast paced work environments to rapid technological advancements and innovations, the challenges we face are diverse and demanding. In such circumstances, our bodies often find themselves in a perpetual state of stress, triggering a response that can impact both our physical and mental health in profound ways.
Understanding the Stress Response
When confronted with stress, our body’s reaction unfolds in three distinct phases: Alarm, Resistance, and Exhaustion.
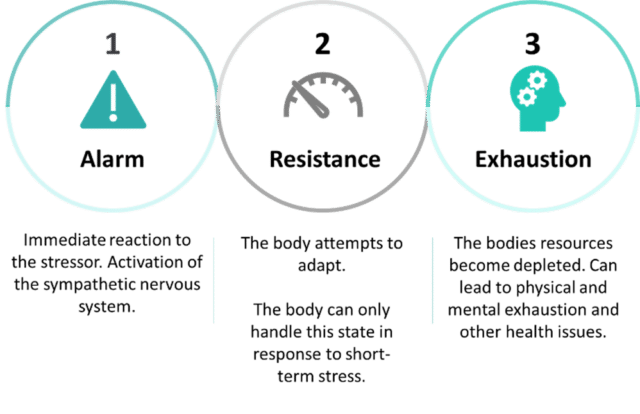
Alarm: This initial phase kicks in swiftly upon encountering a stressor. Whether it’s unsettling news or ongoing uncertainties, our sympathetic nervous system triggers a cascade of hormones like adrenaline, preparing us for fight or flight. This heightened state manifests in accelerated heart rates, increased alertness, and a surge of energy.
Resistance: If stress persists, our body shifts to the resistance stage. Here, hormones like cortisol help sustain our alertness and energy levels. Yet, prolonged exposure to stressors can strain our physical and mental reserves, potentially leading to health issues if left unmanaged.
Exhaustion: Extended stress or multiple stressors over time can push us into exhaustion. This phase depletes our body’s resources, resulting in symptoms such as fatigue, mood swings, and even physical ailments, marking a critical need for intervention and support.
Impacts of Prolonged Stress
The consequences of sustained stress are profound and wide-ranging:
- Decline in Performance: Cognitive abilities and decision-making can suffer under prolonged stress.
- Disengagement and Avoidance: Individuals may withdraw or avoid responsibilities.
- Emotional Instability: Heightened emotional responses become more frequent.
- Physical Manifestations: Health issues like headaches or gastrointestinal problems may arise.
- Increased Substance Use: A reliance on substances to cope may develop.
Strategies for Safeguarding Wellbeing
In the face of prolonged stress, prioritising and adopting proactive strategies is essential to maintaining and safeguarding your personal wellbeing:
Cultivating Positive Self-Belief: Foster a mindset of self-confidence and resilience. Believing in one’s ability to handle life’s challenges can significantly reduce stress and anxiety. Daily affirmations and celebrating achievements, no matter how small, setting realistic goals and acknowledging past successes can bolster confidence amidst challenges.
Maintaining Perspective: Keep challenges in context to avoid magnifying their impact. Understanding that difficult times are often temporary can help maintain a balanced outlook. Practice mindfulness to stay grounded, maintain a broader perspective, recognise that setbacks are temporary and focus on what can be controlled or improved.
Managing Intrusive Thoughts: Intrusive thoughts can fuel anxiety and distort perception. Identifying and challenging these thoughts can prevent them from escalating. Challenge negative thought patterns through mindfulness, meditation, cognitive reframing, or journaling to externalise thoughts and gain perspective.
Establishing Routines & Boundaries: Regular routines and clear boundaries between work and personal life can enhance psychological stability and reduce stress. Create structured daily routines and clear boundaries between work and personal life. Engage in activities that promote relaxation and prevent burnout.
Connecting with Support: Utilise available resources such as Employee Assistance Programs (EAP) or seek support from colleagues and loved ones.
Prioritizing Sleep: Quality sleep is crucial for mental and physical health. The quantity and quality of your sleep can influence how you feel, how you perform activities and how you interact with others. Maintain a regular sleep schedule and practice good sleep hygiene such as reducing caffeine intake in the afternoon and minimising exposure to blue light before bedtime and/or consider the use of a sleep diary.
Nurturing the Mind-Body Connection: Mental health is closely linked to physical health; caring for the body can improve mental wellbeing. Implement lifestyle changes to keep healthy patterns of life such as incorporating regular physical activity into your daily routine, maintaining a healthy and balanced diet and engaging in regular medical check-ups to monitor your health.
Moderating Screen Time: Excessive screen time can lead to information overload, disrupt sleep, and increase stress. Consider substituting activities such as watching TV with going for a walk and limit excessive exposure to screens, especially before bedtime, to mitigate information overload and improve mental focus.
Self-Care Practices: Identify personal activities that promote relaxation and rejuvenation, whether it’s hobbies, meditation, or spending time outdoors. Identify personal self-care activities that help you relax and recharge.
In conclusion, safeguarding wellbeing in challenging work environments requires proactive measures and a holistic approach. By understanding the stages of the stress response and implementing effective strategies, individuals and teams can navigate adversity with resilience and maintain optimal health and performance.



